Introduction
This is a code lab on building a simple application where you can create a Smart Contract Wallet and start sending and receiving tokens without paying any Gas Fees!
At the end of this code lab, we will build an application that returns your Smart Contract Wallet Address, a Form that you can use to send tokens, and a display of the Tokens owned by the Smart Contract Wallet with their respective balances.
FuseBox leverages Account Abstraction out of the Box. It is an Open Source Wallet-As-A-Service platform and is ERC-4337 complaint. Providing Developers the ability to use a Bundler for collacting UserOperations, and also a Paymaster to sponsor Gas payments for their users to provide a Gasless experience.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure you have the following:
- Node.js is installed on your machine.
- Code Editor: Use your preferred code editor; VS Code is recommended.
- An EOA wallet with a private key. You can use an existing one or create a new wallet.
- A basic understanding of React.js and Next.js.
- An API key from the Fuse Console. Get one here.
Step 1: Set Up Your Next.js App
Create a new Next.js app:
npx create-next-app my-fuse-demo-app
cd my-fuse-demo-app
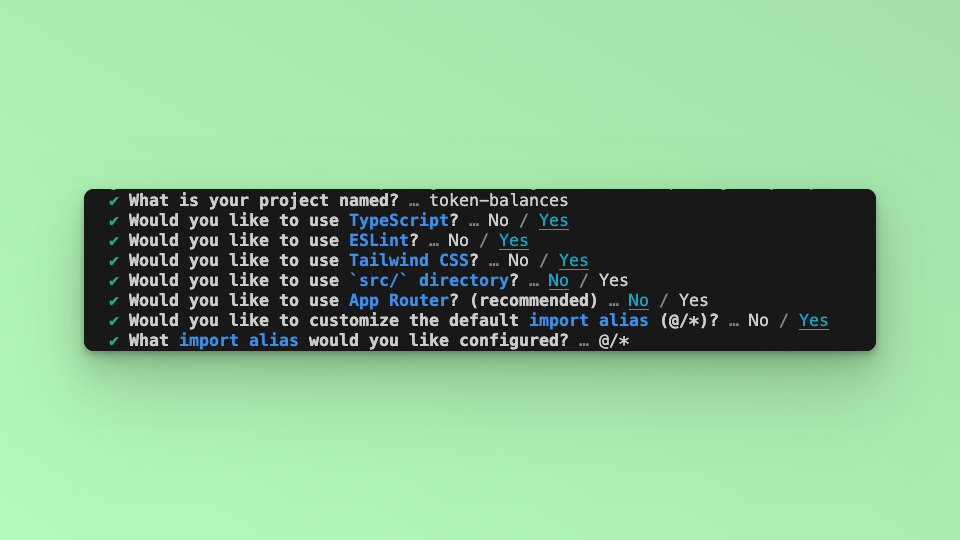
Answer the required prompts from NextJS in the terminal. We must note that we use TypeScript and Tailwind CSS for this application.
Step 2: Install Dependencies
Install the required dependencies:
npm install @fuseio/fusebox-web-sdk
npm install ethers
Step 3: Run the Development Server
Run npm run dev to start the development server. Visit http://localhost:3000 to view your application.
Step 4: Import Libraries
Open the index.tsx file, delete the default code from NextJS. Edit index.tsx file by adding the code below and save it to see the updated result in your browser. First, import the required libraries and put up a default `Hello, World!’ text:
import { FuseSDK } from "@fuseio/fusebox-web-sdk";
import { ethers } from "ethers";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main className={`flex flex-col items-center p-24 ${inter.className}`}>
Hello, World!
</main>
);
}
We are going to use the following FuseBox Web SDK methods to build the application: Create a Smart Contract Wallet. Transfer Token. GET List of Tokens Owned by Address. GET Token Balance.
Step 5: Create a Smart Contract Wallet.
To use the SDK in your project, you must create an instance of the FuseSDK class. This class is the key to interacting with the Fuse API using the SDK.
The init method sets up a wallet and authenticates the user's provided credentials. It requires a API_KEY from FuseBox. Create an Account and get the API_KEY in the Fuse Developer Console here. When you send a request to the server using this method, it verifies the credentials. If the credentials are valid, developers can use the getSender() to return an address.
To create the Smart Contract Wallet, we will update the code by adding a smartWallet function, and parsing the returned Smart Contract Address to a state variable.
Inside the Home Component, import the useState method:
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
Set the state variable to manage the state of the Smart Contract Account that will be created:
const [smartAccount, setSmartAccount] = useState<string>("")
Add the smartWallet function:
const smartWallet = async() => {
const apiKey = "API_KEY";
const credentials = new ethers.Wallet(`0xPrivateKey`);
const fuseSDK = await FuseSDK.init(apiKey, credentials, {
withPaymaster: true,
});
setSmartAccount(fuseSDK.wallet.getSender());
console.log(
`Smart account address: https://explorer.fuse.io/address/${fuseSDK.wallet.getSender()}`
);
}
To call the function and render the response in the application UI, we have to use the setEffect hook to prevent too many re-renders, add the useEffect hook:
import { useState, useEffect } from ’react’;
Add the useEffect Hook:
useEffect(()=> {
smartWallet()
}, [])
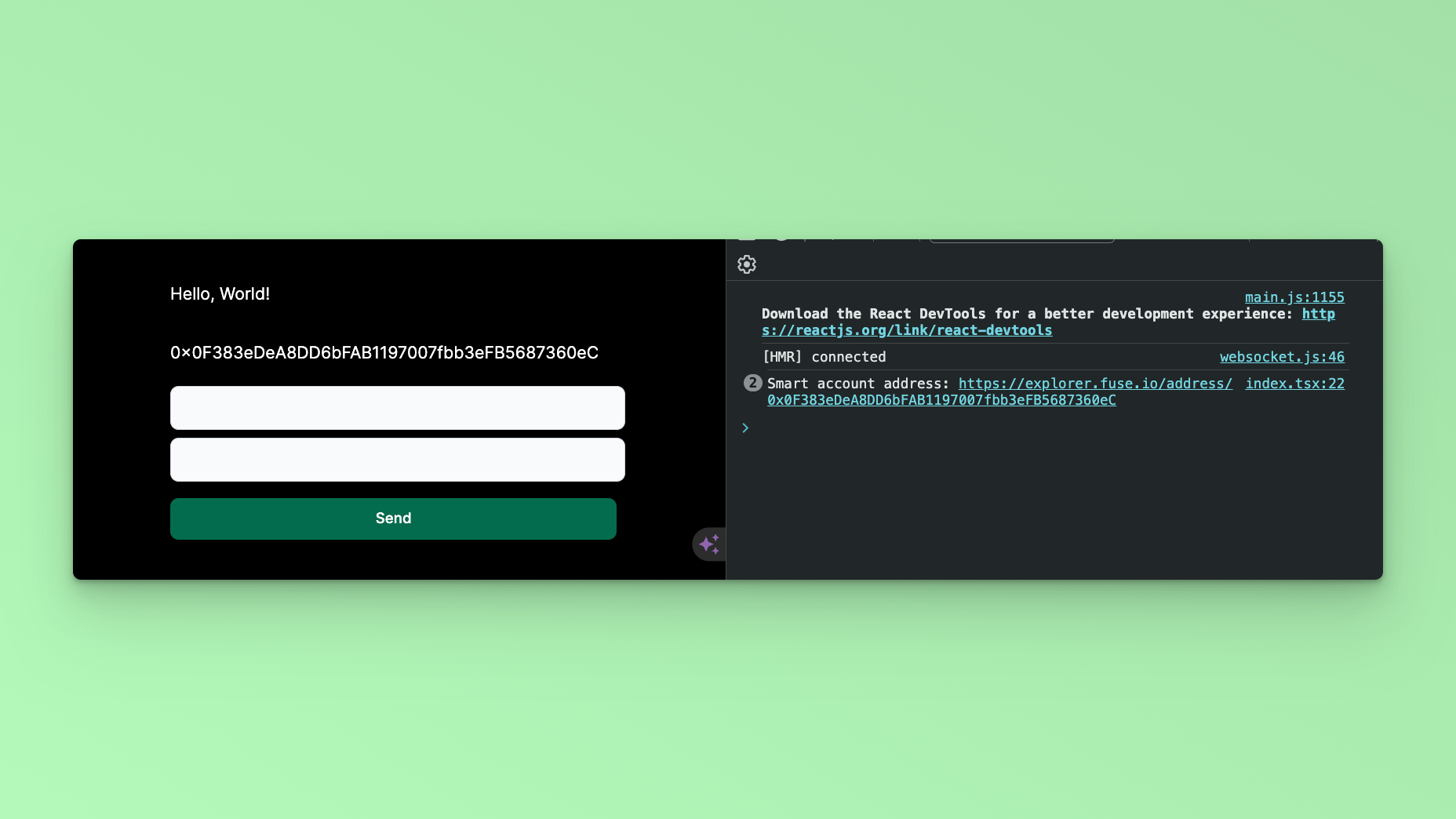
Reload the app and open the console. The newly created Smart Contract Address will be logged into the Console!
To return the Smart Contract Address to the UI, you can parse the stored state variable:
return (
<main className={`flex flex-col items-center p-24 ${inter.className}`}>
Hello, World!
{smartAccount}
</main>
);
Step 6: Token Transfers
Transfer Transactions which happen on the Blockchain are state-changing. In Account Abstraction these “Transactions” are called “UserOperations” because they are first sent to an alternate Mempool where they are then Bundled and sent on-chain. FuseBox uses the transferToken method to carry out a UserOperation of transferring a Token from one Address to another.
Add another Function transferToken:
const transferToken = async() => {
const tokenAddress = "0x28C3d1cD466Ba22f6cae51b1a4692a831696391A"
const apiKey = "API_KEY";
const credentials = new ethers.Wallet(`0xPrivateKey`);
const fuseSDK = await FuseSDK.init(apiKey, credentials, {
withPaymaster: true,
});
const recipient = "Enter ANY EOA or SCA address";
const amount = ethers.parseUnits(amountValue, 6)
const res = await fuseSDK.transferToken(tokenAddress, recipient, amount);
console.log(`UserOpHash: ${res?.userOpHash}`);
console.log("Waiting for transaction...");
const receipt = await res?.wait();
console.log(
`User operation hash: https://explorer.fuse.io/tx/${receipt?.transactionHash}`
);
}
The transferToken method takes in three arguments: tokenAddress, recipient, amount.
The tokenAddress is the address of the Token which we are sending a specific amount to a receiving address recipient. You can find a list of Token Addresses here: https://explorer.fuse.io/tokens
It is important to mention that when sending a Token, you will parse the token in units to the number of the decimal places which the Token is defined. For example, USDC has 6 decimal places. To send 1 USDC, you parse it thus:
ethers.parseUnits(“1”, 6)
Where the string “1” is the amount, and 6 the number of decimal places.
Step 7: Form UI.
To carryout Token Transfer, the next step is to build a Form component where we can enter the recipient and amount values we want to transfer to.
Update the UI:
<form className="flex max-w-md flex-col gap-4">
<div className="mt-3">
<label htmlFor="base-input" className="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-900 dark:text-white" />
<input type="text" id="base-input" className="bg-gray-50 border border-gray-300 text-gray-900 text-sm rounded-lg focus:ring-blue-500 focus:border-blue-500 block w-full p-2.5 dark:bg-gray-700 dark:border-gray-600 dark:placeholder-gray-400 dark:text-white dark:focus:ring-blue-500 dark:focus:border-blue-500" />
<label htmlFor="base-input" className="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-900 dark:text-white" />
<input type="text" id="base-input" className="bg-gray-50 border border-gray-300 text-gray-900 text-sm rounded-lg focus:ring-blue-500 focus:border-blue-500 block w-full p-2.5 dark:bg-gray-700 dark:border-gray-600 dark:placeholder-gray-400 dark:text-white dark:focus:ring-blue-500 dark:focus:border-blue-500" />
</div>
<button type="text" className=" focus:outline-none text-white bg-green-700 hover:bg-green-800 focus:ring-4 focus:ring-green-300 font-medium rounded-lg text-sm px-5 py-2.5 me-2 mb-2 dark:bg-green-600 dark:hover:bg-green-700 dark:focus:ring-green-800">Send</button>
</form>
The Form above has two labels and a button. To use the form, we have to take the input data and pass it as arguments to the transferToken method.
Let’s write the state variables to store the recipient and amount values. In this example, we will keep the tokenAddress static as USDC.
const [toValue, setToValue] = useState<string>(' ');
const [amountValue, setAmountValue] = useState<string>(' ');
Add a handle method to take the input data
const handleTo = (e) => {
setToValue(e.target.value);
};
const handleAmount = (e) => {
setAmountValue(e.target.value)
};
The values are set in the state: recipient == toValue, amount == amountValue
Update the Form UI to handle the data and submit it:
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="flex max-w-md flex-col gap-4">
<div className="mt-3">
<label htmlFor="base-input" className="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-900 dark:text-white" />
<input type="text" id="base-input" **value={toValue} onChange={handleTo}** className="bg-gray-50 border border-gray-300 text-gray-900 text-sm rounded-lg focus:ring-blue-500 focus:border-blue-500 block w-full p-2.5 dark:bg-gray-700 dark:border-gray-600 dark:placeholder-gray-400 dark:text-white dark:focus:ring-blue-500 dark:focus:border-blue-500" />
<label htmlFor="base-input" className="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-900 dark:text-white" />
<input type="text" id="base-input" **value={amountValue} onChange={handleAmount}** className="bg-gray-50 border border-gray-300 text-gray-900 text-sm rounded-lg focus:ring-blue-500 focus:border-blue-500 block w-full p-2.5 dark:bg-gray-700 dark:border-gray-600 dark:placeholder-gray-400 dark:text-white dark:focus:ring-blue-500 dark:focus:border-blue-500" />
</div>
<button type="submit" className=" focus:outline-none text-white bg-green-700 hover:bg-green-800 focus:ring-4 focus:ring-green-300 font-medium rounded-lg text-sm px-5 py-2.5 me-2 mb-2 dark:bg-green-600 dark:hover:bg-green-700 dark:focus:ring-green-800">Send</button>
</form>
Add a handleSubmit method:
const handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
console.log("Input value:", toValue, amountValue);
transferToken();
};
Update the transferToken function to read the values stored in the state:
const res = await fuseSDK.transferToken(tokenAddress, toValue, amountValue);
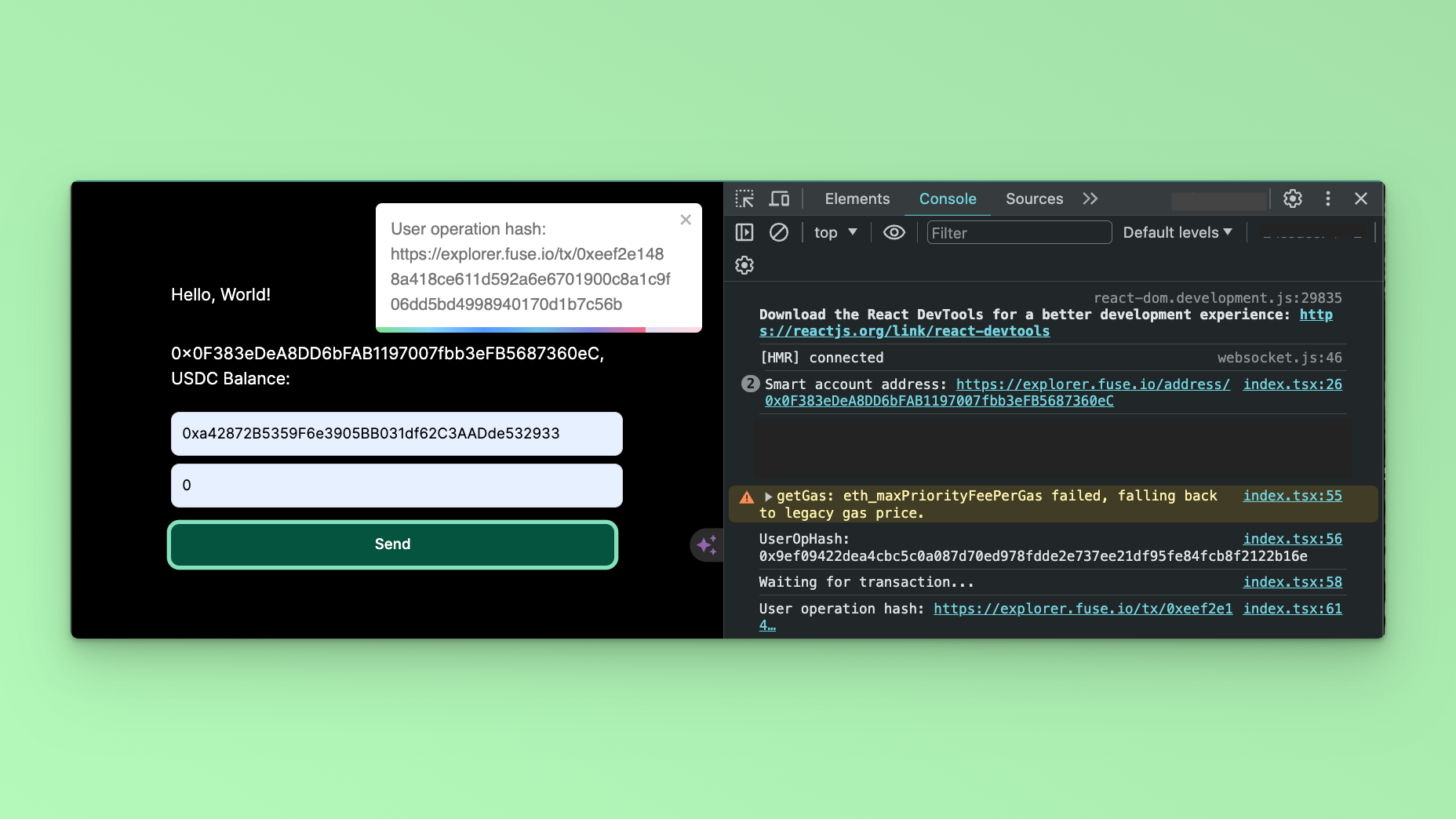
You can carry out Token Transfers via the UI. Note that you have to get some USDC Token, or you can put the number ‘0’ in the amount field to see the success of the UserOperation. You can open the console to see the UserOperation logged.
To see the response returned via the UI, you can use the React Toastify Library. Below is a UI update parsing the Transaction to the UI using the React Toastify library:
First, install the Library:
npm install --save react-toastify
Import the Library:
import { ToastContainer, toast } from 'react-toastify';
Render the Component in the UI at the close of the Form Component
…
<ToastContainer />
…
Add the toast method to the transferToken function.
…
toast("Waiting for transaction...")
console.log("Waiting for transaction...");
const receipt = await res?.wait();
console.log(
`User operation hash: https://explorer.fuse.io/tx/${receipt?.transactionHash}`
);
toast(`User operation hash: https://explorer.fuse.io/tx/${receipt?.transactionHash}`)
…
Conclusion
This tutorial has provided a comprehensive guide on utilizing the FuseBox Web SDK to develop a Demo App for creating Smart Wallet Accounts and executing transfers, all seamlessly integrated with the NextJS UI framework. Throughout the tutorial, we've explored the fundamentals of integrating the FuseBox Web SDK into a Next.js project, including initializing the SDK, managing smart wallet accounts, and implementing transfer functionalities.
This tutorial is a valuable resource for developers looking to harness the power of FuseBox and NextJS to create innovative blockchain-based applications. With the knowledge gained from this tutorial, developers can confidently embark on their journey to build cutting-edge solutions that empower users to interact with digital assets securely and efficiently. To stretch your knowledge, you can use the GET Smart Wallet Token Balance to implement viewing the Balance of the Smart Contract Wallet.
Checkout the complete code. 💻