Introduction
In this tutorial, we'll walk through fetching token balances for an Address using the FuseBox REST API in a Next.js application. We'll utilize React hooks to manage the State and display the token balances in a table format.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the following:
- Node.js installed on your machine.
- Code Editor: Use your preferred code editor. VS Code is recommended.
- An EOA wallet with a private key. You can use an existing one or create a new wallet.
- A basic understanding of React.js and Next.js.
- An API key from the Fuse Console. Get one here.
Step 1: Set Up a Next.js Project
If you haven't already set up a Next.js project, you can create one using the following commands:
npx create-next-app my-project
cd my-project
Answer the required prompts from NextJS in the terminal. We must note that we use TypeScript and Tailwind CSS for this application.
Step 2: Update the UI
In this example tutorial, we are going to build a Form element that takes in any External Owned Address or Smart Contract Address and return its balance in a Table. We will use the Fetch API method to call the Fuse REST APIs and return the responses.
The end point that we will use in this tutorial is the Get Fungible ERC20 Token Balances.
The URL takes in the EOA or SCA, below is an example:
https://api.fuse.io/api/v0/balances/assets/0x07dc9cb1d2f8e7acf92c856cf43467936203f26a?apiKey=API_KEY
Replace API_KEY with your actual apiKey too see the response. Get an API KEY.
Step 3: Fetch the API response.
In this step, we will test calling the API and parsing the response to the web browser console. Add the following code to index.tsx before the return statement.
const apiUrl = `https://api.fuse.io/api/v0/balances/assets/0x07dc9cb1d2f8e7acf92c856cf43467936203f26a?apiKey=API_KEY`;
async function fetchData() {
try {
const response = await fetch(apiUrl);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("Network response was not ok");
}
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error("There was a problem with the fetch operation:", error);
}
}
fetchData();
Save the file.
Run the application using the command:
npm run dev
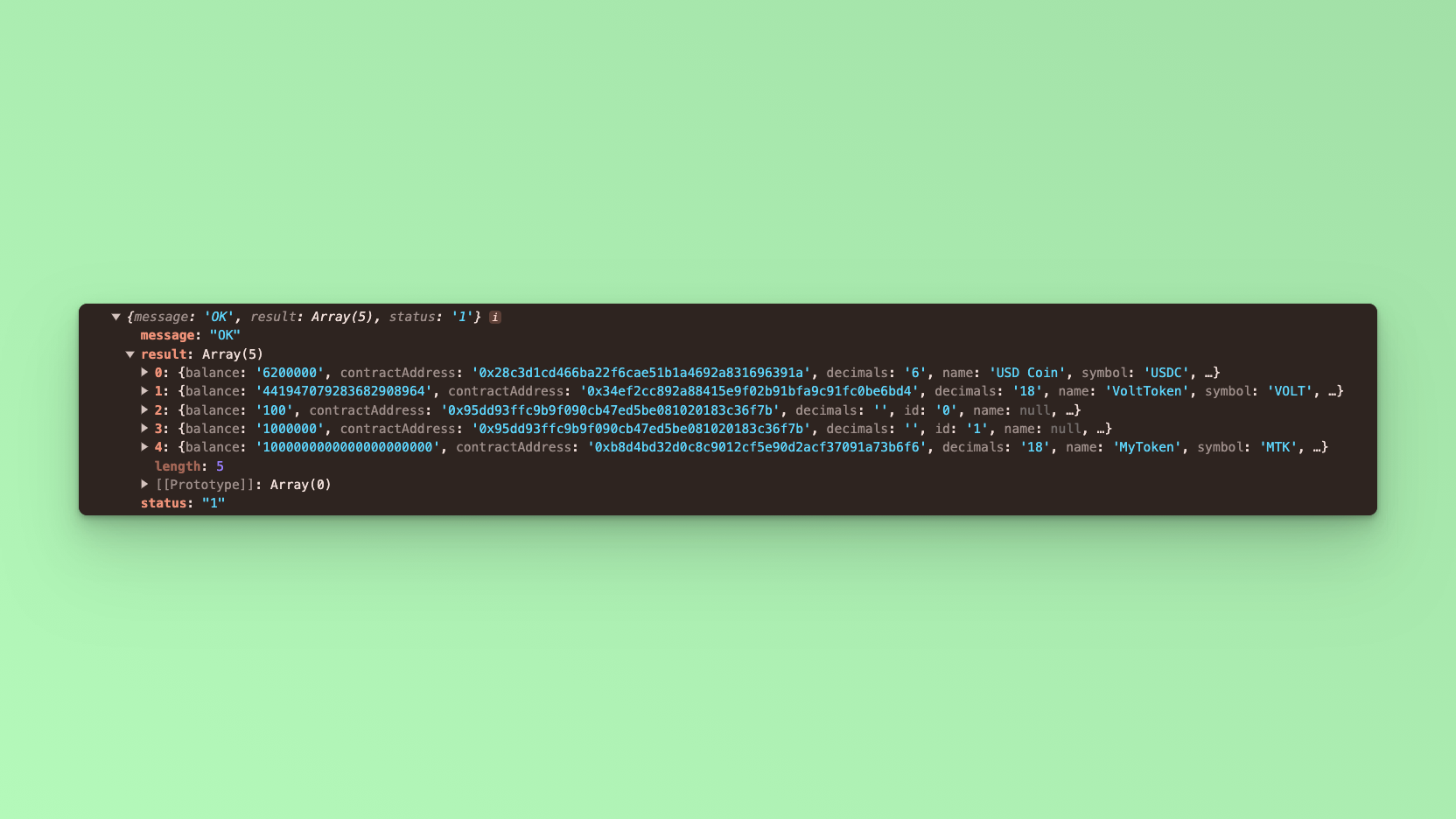
Open your browser go to http://localhost:3000 and open the developer console, you will find the results logged to the console.
Step 4: Table UI
To return the response via the UI, we will use a Table. Copy the code below:
<div className="mt-8 relative overflow-x-auto shadow-md sm:rounded-lg">
<div className="mb-4">Address: {address}</div>
<table className="w-full text-sm text-left rtl:text-right text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-400">
<thead className="text-xs text-gray-700 uppercase dark:text-gray-400">
<tr>
<th scope="col" className="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 dark:bg-gray-800">
Token Symbol
</th>
<th scope="col" className="px-6 py-3">
Contract Address
</th>
<th scope="col" className="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 dark:bg-gray-800">
Balance
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr
key={index}
className={`${
index % 2 === 0 ? "border-b border-gray-200 dark:border-gray-700" : ""
}`}
>
<th
scope="row"
className="px-6 py-4 font-medium text-gray-900 whitespace-nowrap bg-gray-50 dark:text-white dark:bg-gray-800"
>
symbol
</th>
<td className="px-6 py-4">contractAddress</td>
<td className="px-6 py-4 bg-gray-50 dark:bg-gray-800">balance</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
Save the file.
To parse the responses via the UI, we will use React useState to update the UI components. Create an interface to handle the Token response object:
interface Token {
symbol: string
contractAddress: string
balance: number
type: string
}
Create a state to store the responses from the Fetch call using the Token interface.
const [tokenData, setTokenData] = useState<Token[]>([]);
Update the FetchData function by parsing the data response to the state:
setTokenData(data.result);
Update the table body by calling the map() method:
{
tokenData.map((token, index) => (
<tr
key={index}
className={`${
index % 2 === 0 ? "border-b border-gray-200 dark:border-gray-700" : ""
}`}
>
<th
scope="row"
className="px-6 py-4 font-medium text-gray-900 whitespace-nowrap bg-gray-50 dark:text-white dark:bg-gray-800"
>
{token.symbol}
</th>
<td className="px-6 py-4">{token.contractAddress}</td>
<td className="px-6 py-4 bg-gray-50 dark:bg-gray-800">{token.balance}</td>
</tr>
));
}
Save the file.
Step 5: Form UI.
In this step, we add a form component with an input where users can enter any address instead of hard coding it to the URL. Add a form component to the application. Copy and paste the following code snippet directly above the <table> component in your index.tsx file.
<form
onSubmit={}
className="flex max-w-md flex-col gap-4"
>
<div className="mt-3">
<label
htmlFor="address-input"
className="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-900 dark:text-white"
>
Enter Address
</label>
<input
type="text"
id="address-input"
placeholder="Enter Address"
className="bg-gray-50 border border-gray-300 text-gray-900 text-sm rounded-lg focus:ring-blue-500 focus:border-blue-500 block w-full p-2.5 dark:bg-gray-700 dark:border-gray-600 dark:placeholder-gray-400 dark:text-white dark:focus:ring-blue-500 dark:focus:border-blue-500"
/>
</div>
<button
type="submit"
className="focus:outline-none text-white bg-green-700 hover:bg-green-800 focus:ring-4 focus:ring-green-300 font-medium rounded-lg text-sm px-5 py-2.5 me-2 mb-2 dark:bg-green-600 dark:hover:bg-green-700 dark:focus:ring-green-800"
>
Submit
</button>
</form>
Add an event method to take input from the form:
const handleReturnBalances = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
};
Add a state to handle the address from the input. When the address is received from the Form input, it will be parsed to the API URL as a parameter address=${address} replacing the hardcoded address.
const [address, setAddress] = useState < string > "";
Update the apiUrl, use backticks:
const apiUrl = `https://api.fuse.io/api/v0/balances/assets/${address}?apiKey=API_KEY`;
Update the Form Input elements by adding value and onchange arguments. We will set the state when calling onchange:
value={address}
onChange={(e) => setAddress(e.target.value)}
Update the Form submit argument by parsing handleReturnBalance:
onSubmit = {handleReturnBalances};
Before saving the file, move the FetchData call to the handleReturnBalances, so that we can get the response as soon as we hit submit on the Form:
const handleReturnBalances = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
fetchData();
};
Save the file. Run the application using the following command:
npm run dev
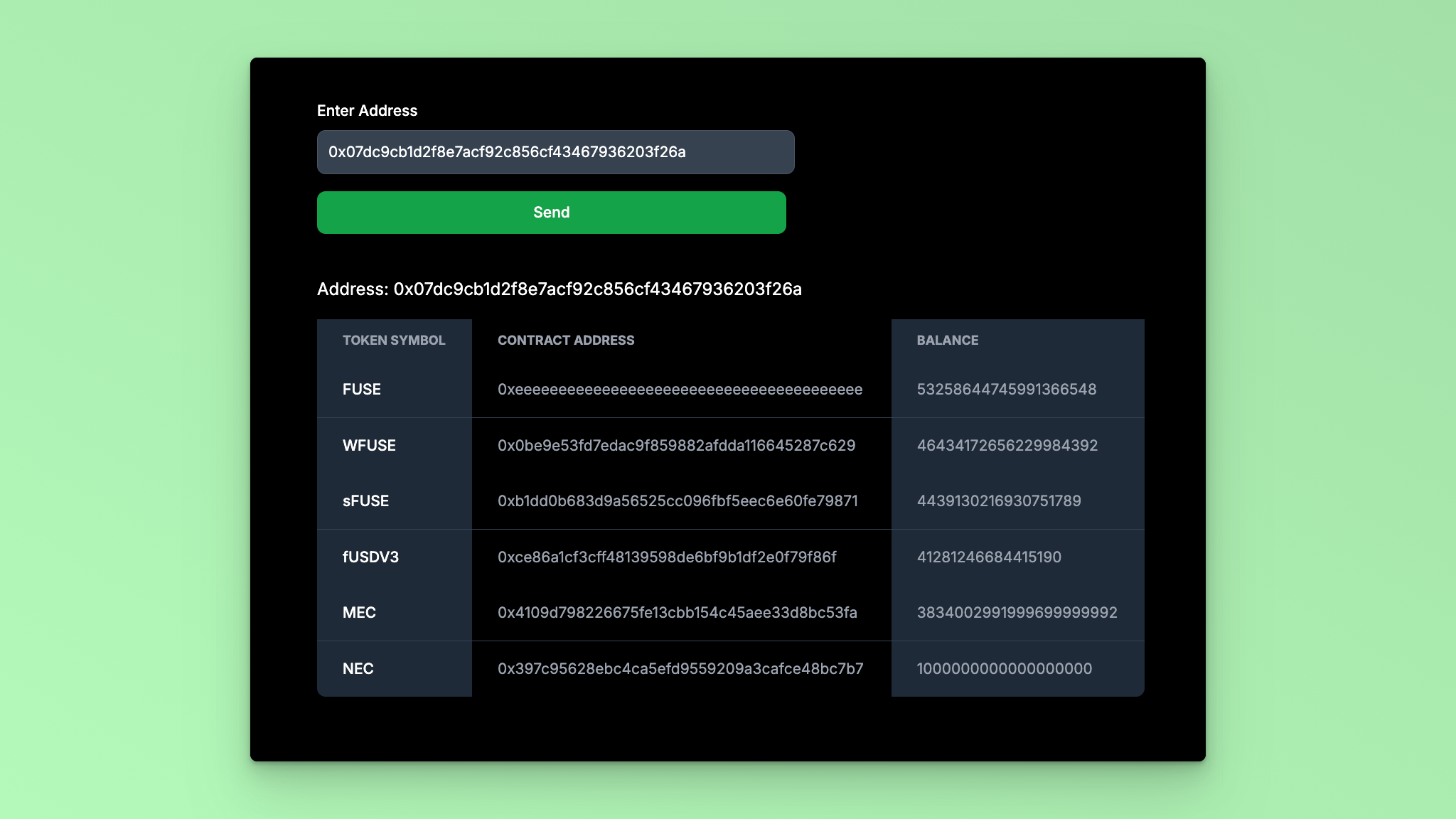
Visit http://localhost:3000 in your browser to see the application in action. You should see a Form. When you enter an address and click Submit, the response will be displayed in a table with the token names, contract addresses, Balance, and token type.
Code Breakdown:
- State variables
addressandtokenDataare initialized using theuseStatehook.addressstores the EOA or SCW address entered by the user, andtokenDatastores the token data fetched from the API. - The
apiUrlvariable is dynamically constructed using template literals. It includes the address entered by the user. - The
handleReturnBalancesfunction is an asynchronous function called when the form is submitted. It prevents the default form submission behavior, and then calls thefetchDatafunction. - The
fetchDatafunction is an asynchronous function that sends a GET request to the API using the fetch function. It checks if the response is ok, then parses the JSON response and updates thetokenDatastate with the fetched data. If an error occurs during the fetch operation, it is caught and logged. - The JSX code renders a form with an input field for the user to enter an Ethereum address. Upon submission, the
handleReturnBalancesfunction is called. The fetched token data is displayed in a table with columns for Token Symbol, Contract Address, Balance, and Token type.
This example code creates a web application that allows users to enter an address, fetch its balances using a REST API, and display the token data in a table format.
Checkout the complete code. 💻